Dependency-Track relies on integration with repositories to help identify metadata that may be useful for the identification of risk. Package repositories to manage and automatically resolve dependencies.
Dependency-Track incorporates the concept of repositories, completely independent of software engineering use-cases, as a way to gain additional intelligence about the components it’s tracking. Dependency-Track brings the power of package repositories to every project the system tracks, whether the project is developed internally or commercial off-the-shelf software.
Dependency-Track supports the following default repositories:
| Ecosystem | Repository | Resolution Order |
|---|---|---|
| cargo | Crates.io | 1 |
| composer | Packagist | 1 |
| gem | RubyGems | 1 |
| github | github.com | 1 |
| go modules | proxy.golang.org | 1 |
| hex | Hex | 1 |
| maven | Maven Central | 1 |
| Atlassian Public | 2 | |
| JBoss Releases | 3 | |
| Clojars | 4 | |
| Google Android | 5 | |
| npm | NPM | 1 |
| nuget | NuGet | 1 |
| pypi | PyPI | 1 |
| cpan | CPAN | 1 |
Additional repositories can be added for each supported ecosystem. Additionally, repositories can be enabled or disabled as well as identified as ‘internal’. A username and/or password may be specified, which allows Dependency-Track to scan packages from private repositories that require basic authentication, like Azure Artifacts or Artifactory.
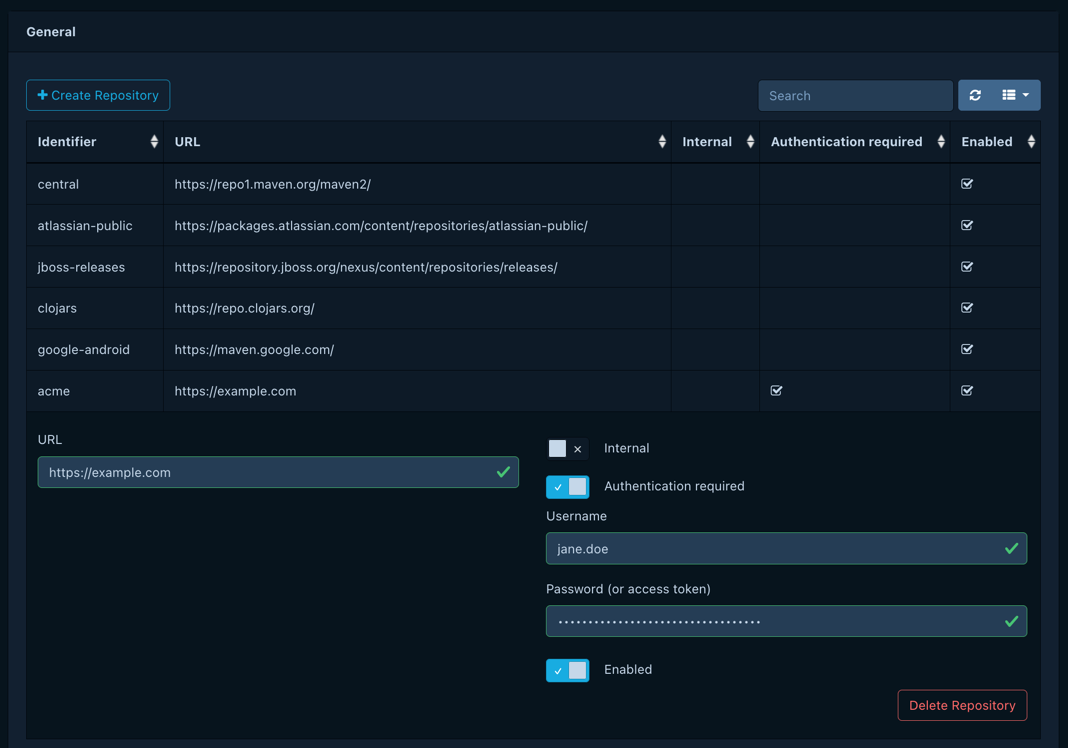
Components that are identified as ‘internal’ will only be analyzed using ‘internal’ repositories. Non-internal components will only be analyzed using non-internal repositories. Disabled repositories will be omitted from component metadata analysis.
Outdated Version Tracking #
One primary use-case for the support of repositories is the identification of outdated components. By leveraging tight integration with APIs available from various repositories, the platform can identify outdated versions of components across multiple ecosystems. Dependency-Track relies on Package URL (PURL) to identify the ecosystem a component belongs to, the metadata about the component, and uses that data to query the various repositories capable of supporting the components ecosystem.
Package URL is natively supported in the CycloneDX BOM specification. By using CycloneDX as a means to populate project dependencies, organizations benefit from the many use-cases Package URL provides, including leveraging repositories to identify outdated components.
Refer to Datasource Routing for information on Package URL and the various ways it is used throughout Dependency-Track.
Authentication #
GitHub
For GitHub repositories (github.com per default), the username should be the GitHub account’s username,
and the password should be a personal access token
(PAT) with public access (no additional scopes).

 v4.13
v4.13