Notice
This is a preview feature only. Data may not be fully synchronized. Doing backup is recommended before enabling it.
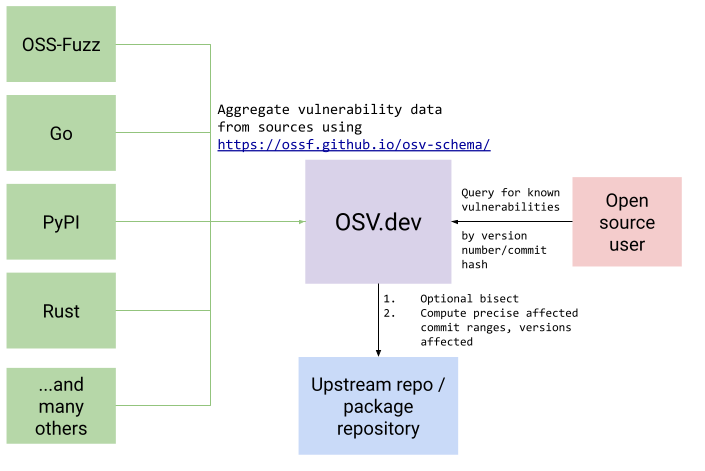
Open Source Vulnerabilities (OSV) is a vulnerability database and triage infrastructure for open source projects aimed at helping both open source maintainers and consumers of open source. This infrastructure serves as an aggregator of vulnerability databases that have adopted the OpenSSF Vulnerability format.
OSV additionally provides infrastructure to ensure affected versions are accurately represented in each vulnerability entry, through bisection and version analysis.
Dependency-Track integrates with OSV by mirroring advisories from GCS bucket maintained by OSV gs://osv-vulnerabilities.. The mirror is refreshed daily, or upon restart of the Dependency-Track instance. No personal access token is required to authenticate with OSV.
Ecosystems #
User can select specific ecosystems to mirror vulnerabilities from OSV. Ecosystems need to be selected (per requirement) in order to enable OSV feature. Debian ecosystem package is superset of all individual versions, it is suggested to enable Debian alone instead of all Debian versions.
NOTE: Disabling the OSV would remove current ecosystem selection, but already mirrored vulnerabilities would be retained.
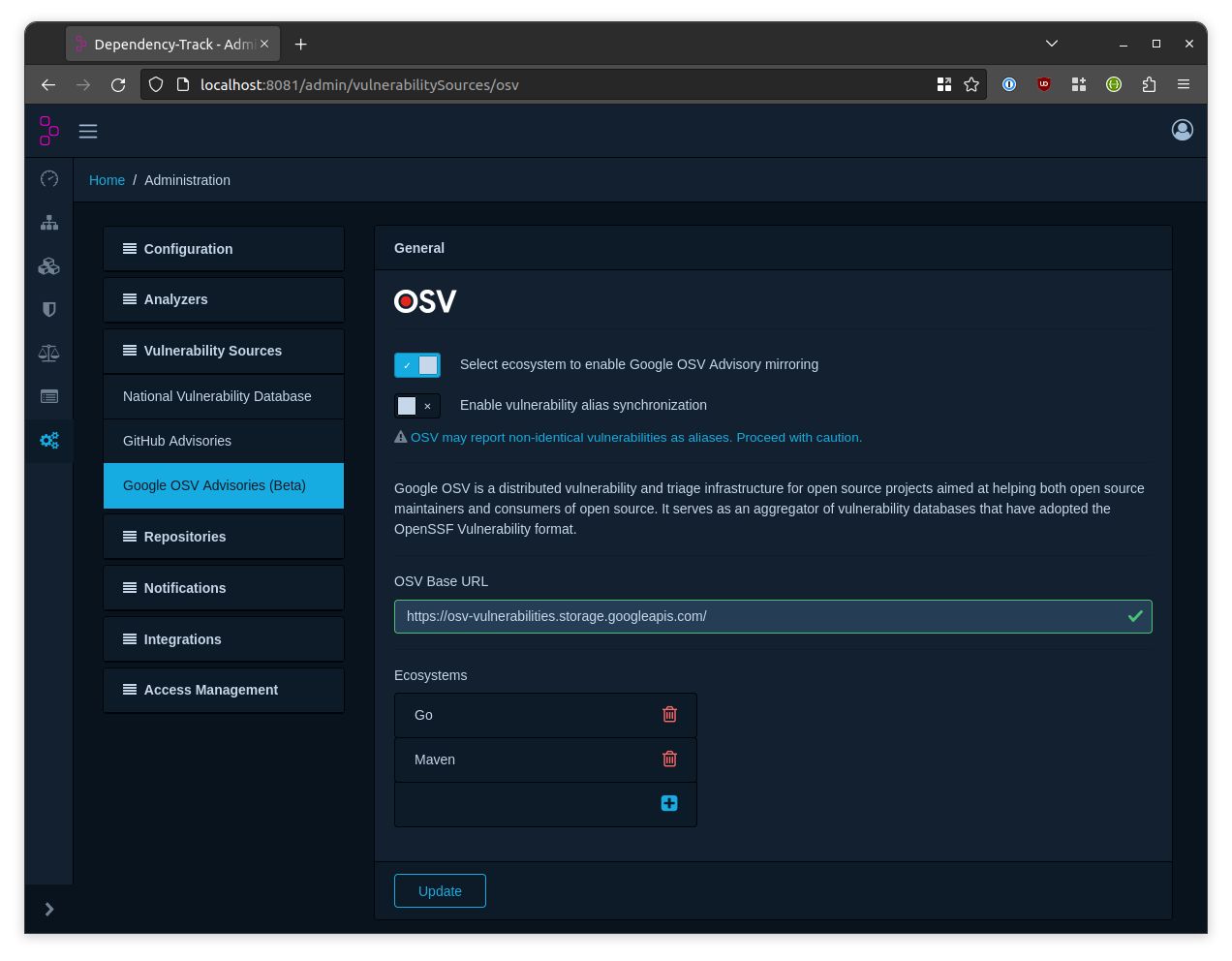
This integration will enable vulnerability DB of selective ecosystems in DT (as shown). It can be also used in an offline mode (without having internet access to the DT API server).
Current defined ecosystems are below. Updated list can be found at https://osv-vulnerabilities.storage.googleapis.com/ecosystems.txt.
| Ecosystem | Description |
|---|---|
| Go | The Go ecosystem |
| npm | The NPM ecosystem |
| OSS-Fuzz | For reports from the OSS-Fuzz project that have no more appropriate ecosystem |
| PyPI | the Python PyPI ecosystem |
| RubyGems | The RubyGems ecosystem |
| crates.io | The crates.io ecosystem for Rust |
| Packagist | The PHP package manager ecosystem |
| Maven | The Maven Java package ecosystem |
| NuGet | The NuGet package ecosystem |
| Linux | The Linux kernel |
| Debian | The Debian package ecosystem; The ecosystem string might optionally have a : |
| Hex | The package manager for the Erlang ecosystem |
| Android | The Android ecosystem |
| GitHub Actions | The GitHub Actions ecosystem |
| Pub | The package manager for the Dart ecosystem |
Vulnerability Aliases #
The OSV schema allows vulnerability databases to express if the same vulnerability is present in other databases as well, and what its identifiers in those databases are. The OSV aliases field is intended for this purpose.
While most of the time only truly identical vulnerabilities are listed in aliases, there are multiple cases
where related vulnerabilities are listed, too. Alias support in Dependency-Track however is based on the
assumption that vulnerabilities reported as aliases are indeed identical.
Thus, as of Dependency-Track v4.8.0, synchronization of alias information from OSV (and other sources that provide it), can be selectively turned off. For OSV, synchronization is disabled per default. Enabling it is not recommended at this point in time.
 v4.13
v4.13